Amongst all-natural fibers, flax is the oldest fiber crop in the world. Flax is also known as Linen. In article, we will know everything about flax fiber.
Table of Contents
What is Flax Fiber?
Flax is the most popular bast fiber. Binominal name of flax is Linum Usitissumum. We get this fiber from the stalk of a plan. Amongst all-natural fibers, flax The Flax fiber is classified as natural, cellulosic, bast, and multicellular fiber. we can call linen flax.

Lilen is the term applied to the yarn spoon from the flax fibers. Flax was probably the first plant fiber to be used by man for making textiles at least in the western hemisphere and traditionally used for bed sheets, underclothes, and table linen.
Composition of Flax
- Cellulose: 76%
- Wax: 2.5%
- Lignin:2.7%
- Protein:2.5%
- Pectin’s: 2.0%
- Ash: 0.8%
- Unidentified parts:13.5%
Production region/ Producing countries/ origin of flax: Belgium, China, France, Russia, Ireland, Netherlands, and Canada.
History of Flax
About 5000 years ago, flax was cultivated in India and China. From prehistoric times we use fabrics, which is made from flax fiber. In ancient Egypt, flax was cultivated. In Egypt, the temple walls were paintings of flowering flax. At that time, flax fiber was considered a symbol of purity, that’s why Egyptian priests wore linen only.

Egyptian linen was traded by the Phoenicians. Mediterranean and Romans used it for their sails. As the Roman Empire declined, so did flax production. In the middle ages, Eventually, Flanders became the major center of the European linen industry. In North America, flax was introduced and flourished by colonists. During the 17th century, in many Western Europe, linen manufacture was established as a domestic industry.
Production
Flax fiber is cultivated on a commercial scale in Russia, Belgium, Holland, England, and Ireland.
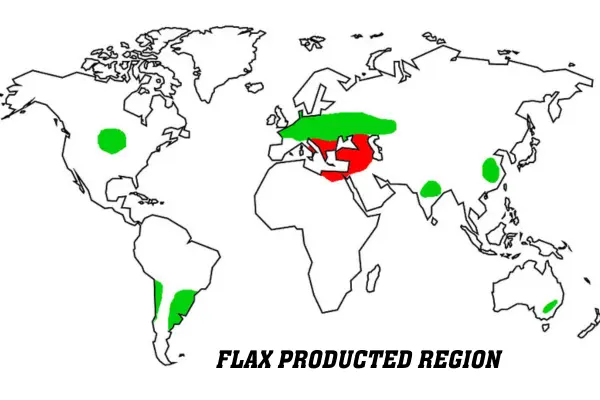
The most valued variety is Courtrai flax, which is contained in Belgium. In 2020, Kazakhstan produced 3.4 million tonnes of flax.
Flax cultivation process:
- First, the land is plowed to a greater depth in the winter season ( March & April)
- Then seeds are sown.
- Irrigation is required
- Pest and diseases should be controlled.
- After approximately 100 days, flax is harvested for fiber production.
Production grows two types of flax:
- Seed flax
- Fiber flax
Requirements for flax seed cultivation:
Flax is a cool weathered/ winter crop. This crop thrives well in both alluvial soil of the north and south peninsular region. However, it grows well in soil which can retain moisture in the cold season. As the roots of flax penetrate deep into the soil, the land should be ploughed to a greater depth. This crop requires 50 – 60 % humidity with 7 inches of rain.
Atmosphere:
It needs plain and well-plowed land and a moist climate to cultivate flax. Mineral water is needed for cultivation.

Flax seed is a cold-season crop grown in both the northern and southern regions of India. It is also grown in loamy deep soil which is fertile, silty, and well-drained. Flaxseed can be sown as per utera system of cropping, sowing flaxseeds before harvesting of standing paddy crop so that it will utilize moisture efficiently under a rainfed agro-ecosystem. Flax crop requires a relative humidity of 50-60% with 7-8 inches of rain.
Land preparation
Flax fiber roots go deeper into the soil, so prepare the land by proper deep plowing. 2-3 ploughings can be done.
Sowing of Flaxseed
The required seed rate for this crop is 30-40 seeds kg/ha. Seeds can be sown according to the line sowing method with uniform distribution. Seeds must be placed 4-5 cm below the soil.
Spacing between each row can be kept as 20-30 cm and between each crop can be kept as 10 cm. The moisture level must be good as this crop requires more moisture. Make sure moisture is maintained in the germination phase and in each development phase, so proper irrigation practices must be done.
Retting:
Since the bast fibers are an integral part of the stem structure, they are not directly available for spinning.

They must be separated from the other issues by a process, which is known as retting. There are various methods of retting such as
- Dam Retting
- Water Retting /Tank Retting
- Dew Retting
- Chemical Retting
Dam Retting:
The flax plants after being cut down are tied up in sheaves or beets and immersed for about 10 days in water in special dams or ponds dug into the ground. This method is no longer practiced in Egypt. This method is commonly used in Ireland.
Water Retting:
In water retting, the stalks are tied in bundles and covered with water in a tank. Putrefactive fermentation is caused by bacteria. This gradually softens the stems by destroying the less-resisting issues and rendering the intercellular adhesive substance soluble. When the fermentation has reached the appropriate stage, the flax fibers can be separated quite easily. This operation takes about 3 weeks.
Dew Retting:
Dew retting is similar in action to water retting but slower. Sometimes water retting starts the fermentation and the stalks are then taken out and laid on the grass to complete the process. It may be used in regions where water is in short supply. It is commonly practiced in Russia and Europe.
Chemical Retting:
Chemical retting consists of softening the tissues by boiling them with diluted oxalic acid or alkali either in the atmosphere or at high pressure. It is more costly than biological getting.
Harvesting and fiber extraction process:
Cutting / Pulling
⬇️
Rippling/ Roughing out
⬇️
Retting
⬇️
Drying
⬇️
Breaking
⬇️
Scotching
⬇️
Hacking
Cutting method: The mature plant is cut from the ground with moving mechanized equipment and racked with the bundle.
Pulling method: The mature plant is pulled out from the ground including the roots to maximize the fiber length.
Retting: Retting is the process that softens and separates the fibrous matter from the outer layer of woody matter. It is carried out in the following ways:
- Dam or pond retting: The flax is immersed in the water of a pond or dum for about 10 days.
- Dew or field retting: The flax is spread on a large field and allows due to collect on it. This process normally takes a month or more.
- Tank retting: The flax is placed in tanks of warm water for about 5 to 8 days.
- Chemical retting: The flax is treated with chemical reagents such as caustic soda, sodium carbonate, dilute mineral acids, etc.
- Enzyme retting: Flax stalks are immersed in an enzyme mixture for 12 to 24 hours. The process is faster and cleaner.
- Drying: Drying of the flax fiber is done by means of warm air in cold countries or sunlight in hot countries.
Dressing: Dressing of the flax fiber means to remove the straw from the fibers. It consists of 3 steps:
- Breaking: The process of breaking up the straw into short segments is called breaking. The flax is passed between fluted rollers in a breaking machine to break the stem without damaging the fibers.
- Scotching: The process of separating the unwanted woody matter from the fiber is called scotching.
- Hackling: The process of separating the long line fibers from shorter tows is called hacking.
Construction of flax:
Microstructure of flax
The morphological structure or Microstructure of flax is as follows:
- Elementary fiber
- Technical fiber
- Flax stem
- Meso fibril
- Micro fibril
Fig. Micro- Structure of flax fiber
Macro – Structure of flax:
- The average length is 50 cm.
- Flax fiber is a strand of cells.
- About 3 to 6 ultimate cells constitute.
- Diameter ranges from 40 – 80 mm.
- The color is light blonde to grey-blonde.
Physical properties:
- Length: Average length 45-60 cm
- Maximum length 100cm.
- Length to breadth ratio: For the longest flax, the breadth ratio is 15000:1. For short flax breadth ratio is 15000:1 or less.
- Handle and appearance: Its surface is Rough.
- Color and Iusture: It is brownish or yellowish, white or grey in color. It has natural Iusture.
- Elasticity: Flax is an elastic fiber.
- Effect Of Moisture: 12%
- Specific Gravity:1.54
- Thickness: 40 – 80 mm
- Extensibility: 2%
- Specific gravity: 1 .54
- Cross–section: Polygonal
- Moisture regain: 12%
- Color: light blonde to brown
- Strength: 57.4 cN/ tex
Chemical properties:
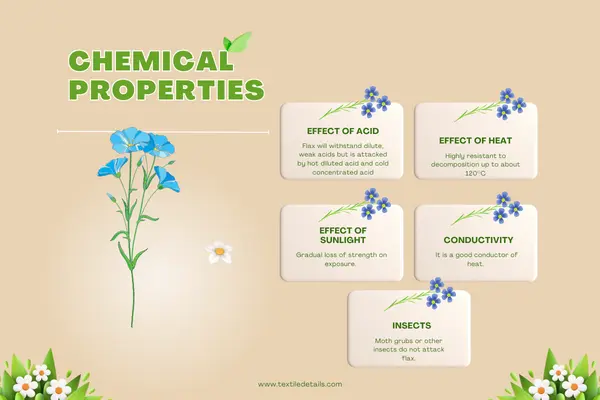
- Effect of Acid: Flax will withstand dilute, weak acids but is attacked by hot diluted acid and cold concentrated acid.
- Effect of alkali: Flax has good resistance to alkaline solution.
- Effect of bleaches: Flax is more difficult to bleach than cotton. Sodium hypochlorite and sodium perborate are used as bleaching agents.
- Effect of heat: Highly resistant to decomposition up to about 120°C
- Effect of Sunlight: Gradual loss of strength on exposure.
- Conductivity: It is a good conductor of heat.
- Insects: Moth grubs or other insects do not attack flax.
- Effect of micro-organism: Flax has resistance to microorganisms.
Thermal properties:
Flax has the best heat resistance and conductivity of all commonly used textile fibers. The polymer system of flax is highly crystalline. The long polymers contribute to the tenacity and durability of the fiber.
- Chemical Composition:
- Cellulose: 75%
- Hemi- cellulose: 5 %
- Lignin: 4 %
- Fat/ Wax : 3%
- Ash: 0.5 %
- Water: 12.5 %
Identification of flax:
- Burning test: Flax is easily dissolved in 70 % H2so4 at 38º in minutes.
- Microscopic view: Flax fiber can be identified by nodes in longitudinal view and polygonal cross–section.
Polymer system:
- The chemicals same as the cotton polymer but physically differs from cotton.
- The polymer is about 18000 mm long and 0.8 nm thick.
- The degree of polymerization (DP) is about 18000.
- Every polymer chain has 18000 cellobiose units.
- Polymer chain spiral about its axis at 6º angle.
Cottonized of flax:
The process of breaking down the fiber bundles to their ultimate by mechanical or chemical means is called cottonized flax. The broken fluxes are called cottonized flax. The length of cottonized flax is about 25 to 40 mm.
The object of cottonizing is to reduce the length of the fiber to make it suitable for cotton machinery.
Application of Flax Fiber
Apparel: Shirt, suits, jackets, trousers, skirts, leisure and summer wear.
Accessories: Pockets, bags, shoes.
Home Textiles: Bed clothing, tablecloths, furniture.
Industrial textiles: Ropes, sewing thread.
The principal physical characteristics of flax which distinguish it from other fibers:
- Rapid absorption and disruption of moisture.
- High crystallinity of the cellulose component of the fiber.
- Low extensibility of flax yarns.
- High tenacity of fibers and yarns.
- The high luster of lignin fabrics.
Reference:
- http://plantarchives.org/pdf%2015-2/711-716%20(2973).pdf
- http://www.dissertations.wsu.edu/Thesis/Spring2007/j_mcnassar_042707.pdf
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Flax
- https://homescience10.ac.in/storage/pages/ecurriculum/Msc%20(C&T)%20Sem%201/Fabric%20Science/FLAX%20(LINEN).pdf
- https://www.textilestudent.com/properties-of-flax-fibers
- https://www.slideshare.net/butexpranob/flax-60398039
- https://www.exportersindia.com/product-detail/flax-seed-4562387.htm
- https://www.agricultureinformation.com/forums/threads/flax-plant-cultivation.58836
- https://www.studocu.com/my/document/universiti-teknologi-mara/technology-textiles/a-summary-of-flax-txl129/39728206
