An industrial washing and dyeing machine is essential for all kinds of cotton, jeans, sweaters, silk, and blinded fabric to wash and dye.
In the realm of textile manufacturing, attaining the utmost level of dyeing efficiency and quality holds utmost importance. The washing and dyeing machine emerges as a crucial component in this intricate process. This article will delve into the functions of washing and dyeing machines, and their significance in the textile industry.
Table of Contents
How Does a Washing Machine Work?
Basic Principles of Washing
Washing and dyeing machines are a fundamental part of textile wet processing. They operate on the simple but effective principles of mechanical action, chemical action, and thermal action. Mechanical action involves the movement of the fabrics, causing friction and facilitating the removal of dirt and stains.
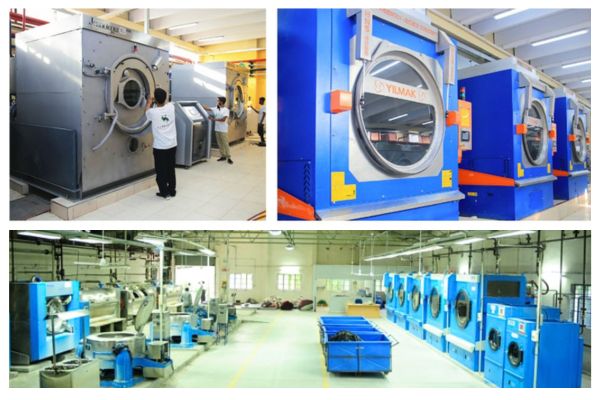

Chemical action involves the use of detergents and chemicals to break down and remove stains. Thermal action, uses heat to enhance the cleaning process.
Types of Washing Machines
There are various types of washing machines, each designed for specific task. The most common types include batch washers, continuous washers, and open-width washers.
- Batch washers are used for small loads and provide a more controlled environment for washing.
- Continuous washers are designed for larger quantities and continuous processing.
- Open-width washers are ideal for fabrics that can’t be folded.
Main Function of Dyeing Machine
- Dyeing machine special-designed drum for low liquor ratio, save water consumption.
- The inner drum has the capability to automatically rotate in both forward and reverse directions.
- Multiple steam inlet, direct stable, and uniform heating.
- Door safe device, once open the front door, the machine will stop automatically.
- Digital timer and temperature control.
- Pneumatic steam inlet, pneumatic water draining.
Washing and Dyeing Machine Function
Combining Washing and Dyeing
Washing and dyeing machines are designed to streamline the entire textile processing cycle. These machines combine the functions of washing and dyeing, reducing the need for multiple processes and handling.

This integration results in significant time and resource savings, making production more efficient.
Key Components of a Washing and Dyeing Machine
Washing and dyeing machines consist of several key components. These include a loading compartment, where fabrics are placed, and an inner drum where the washing and dyeing processes occur. They are equipped with a water inlet and outlet, as well as heating elements to control temperature. A control panel allows operators to set various parameters for washing and dyeing.
Machine Parameter of Washing and Dyeing
| Models | XGP- 50 | XGP- 80 | XGP- 100 | XGP- 150 | XGP- 200 | XGP- 360 | XGP- 450 | XGP- 550 | XGP- 600 | XGP- 800 | XGP- 1000 | |
| Capacity | lbts | 50 | 80 | 100 | 150 | 200 | 360 | 450 | 550 | 600 | 800 | 1000 |
| Drum diameter | mm | 660 | 710 | 850 | 950 | 950 | 1066 | 1066 | 1220 | 1280 | 1400 | 1280 |
| Drum length | mm | 610 | 850 | 900 | 1100 | 1530 | 1880 | 2270 | 2270 | 2270 | 2390 | 3330 |
| Drum volume | lt. | 210 | 330 | 510 | 780 | 1080 | 1650 | 2000 | 2650 | 2900 | 3650 | 4250 |
| Inner thickness | mm | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
| Gap between drums | mm | 25 – 30 | 25 – 30 | 25 – 30 | 25 – 30 | 25 – 30 | 25 – 30 | 25 – 30 | 25 – 30 | 25 – 30 | 25 – 30 | 25 – 30 |
| Spin speed | rpm | 40 | 40 | 40 | 38 | 38 | 38 | 38 | 38 | 38 | 38 | 38 |
| Steam connection | θ | DN 25 | DN 25 | DN 25 | DN 25 | DN 25 | DN 25 | DN 25 | DN 25 | DN 25 | DN 25 | DN 25 |
| Water connection | θ | DN50 | DN50 | DN50 | DN50 | DN50 | DN80 | DN80 | DN80×2 | DN80×2 | DN80×2 | DN80×2 |
| Steam max pressure | Bar | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 |
| Water max pressure | Bar | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Air max pressure | Bar | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| Power of motor | KW | 0.75 | 1.1 | 1.5 | 2.2 | 3 | 4 | 5.5 | 7.5 | 7.5 | 11 | 11 |
| Voltage | Volt/Hz | 380/50 | 380/50 | 380/50 | 380/50 | 380/50 | 380/50 | 380/50 | 380/50 | 380/50 | 380/50 | 380/50 |
| Water consumption | L | 150 | 230 | 280 | 400 | 500 | 850 | 950 | 1200 | 1300 | 1700 | 2300 |
| Steam consumption | Kg/h | 18 | 31 | 42 | 60 | 77 | 140 | 164 | 182 | 218 | 291 | 364 |
| Machine length | mm | 1260 | 1550 | 1650 | 1850 | 2250 | 2900 | 3350 | 3350 | 3350 | 3500 | 4400 |
| Machine width | mm | 1170 | 1220 | 1450 | 1700 | 1700 | 1840 | 1850 | 1950 | 2100 | 2100 | 2100 |
| Machine height | mm | 1200 | 1600 | 1600 | 1600 | 1700 | 1800 | 1800 | 1950 | 2150 | 2400 | 2150 |
| Machine weight | kg | 300 | 400 | 500 | 700 | 1000 | 1400 | 1600 | 1800 | 1950 | 2350 | 2500 |
Optional Function
- Inverter
- PLC touch screen control
- Pneumatic breaking system
- Auto finding door system
- Low water level internal barrel designed
- Automatic water flow meter
- Indirectly heating
- Automatic mixing and feeding tank system
The Science Behind Dyeing Machines
Dyeing as a Process
Dyeing is the process of adding color to fabrics, and garments giving them their unique appearance. This process involves several steps, including wet preparatory, dyeing, and finishing. The preparation phase ensures that the fabric is ready to accept the dye.
The dyeing phase involves the application of the chosen color, and the finishing phase sets the dye to prevent fading.
Types of Dyes and Their Role
Textile dyeing utilizes various types of dyes, such as direct dyes, reactive dyes, acid dye, azoic, vat dyes and disperse dyes. Each type of dye has specific characteristics and is suitable for different fabrics. For example:
- Direct dyes are used for cellulose-based fibers
- While reactive dyes are perfect for protein-based fibers.
- Disperse dyes are commonly used for synthetic fibers.
Benefits of Using These Machines
1. Efficiency in Production
Washing and dyeing machines significantly improve production efficiency. By combining the two processes, manufacturers can reduce the time required to complete textile treatment. This results in a faster turnaround and increased productivity, meeting market demands more effectively.
2. Quality of Enhancement of the Garments
These machines also contribute to the overall quality of the washed garments. The integrated washing and dyeing process ensures uniformity in color and fabric quality. The controlled environment and precise parameters lead to consistent results, reducing the chances of defects and inconsistencies in the textiles.
Common Issues and Maintenance
Troubleshooting Washing and Dyeing Machines
Like any industrial equipment, washing and dyeing machines may encounter issues. Common problems include water leakage, temperature fluctuations, and electrical malfunctions. Regular maintenance and troubleshooting by trained personnel can address these issues effectively.
Tips for Maintenance
To ensure the longevity and optimal performance of washing and dyeing machines, textile engineers should follow a routine maintenance schedule. It includes cleaning regularly, lubrication, and inspection of key components. Properly maintained machines are more reliable and cost-effective dyeing operation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, washing and dyeing machines play a crucial role in the textile industry. They combine the essential processes of washing and dyeing, resulting in increased efficiency and improved garments quality. As textile manufacturing continues to evolve, these machines will remain indispensable in meeting the demands of the market.

Mahedi Hasan working as an Executive (Fabric Marketing) at Pengnuo Group. Graduated with B.Sc. in Textile Engineering. Before was a Top Rated content writer at Upwork, and Level 02 Seller at Fiverr, Level 02 Publisher at Ezoic. Very passionate about content writing, SEO practice, and fashion website designing. Highly Experienced fashion writer for the last 4+ years. Have extensive 7 years of experience in the wholesale clothing business.
