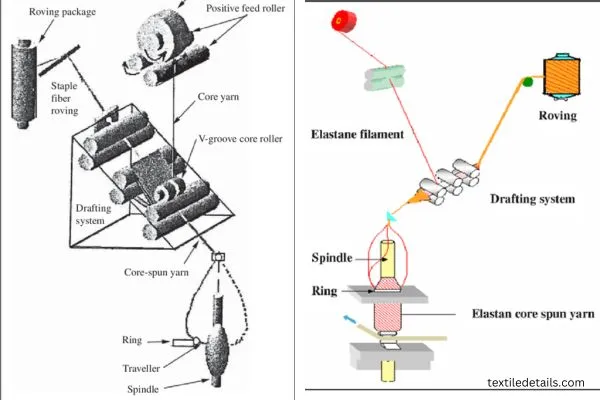
In the textile industry, core spun yarn is one of the most important concepts. The process of core-spinning is by twisting the fibers around a filament or an existing yarn which produces a sheath-core structure.
Core and sheath are the two components in the core spun yarns. The staple fibers are used as the sheath covering, while the continuous filament yarn is used as the core. This process enhances the functional properties of any fabric. Properties such as durability, tensile strength, and comfort are enhanced.
In this article, we will talk about the core spun yarn manufacturing process.
What is Core Spun Yarn Made of?
The core-spun yarn is also known as the poly core. Existing staple fibers are twisted around a core that produces the yarn. This process is also known as the “Polycore” because “poly” means polyester, which is added to the yarn to strengthen it.
The denim industry uses most yarn because denim products need the most stretchability. To enhance the stretchability of the denim items, yarn is being used. The yarn is also known as the “cotton core” because it adds softness and durability to the product.
Core Spun Yarn Manufacturing Process
The process does not require a lot of steps, and it is relatively easy. Here is how it is executed.
Step – 1: Opening and Cleaning
The first step is to make the short fibre form into a uniform fibre roll, known as the opening and cleaning process. This creates conditions for the carding process. This step is crucial as it ensures that the entire batch of short fibers can have the same color and strength when spun into the thread. Around a filament, any cotton or polyester material is wrapped at first to start the core spinning process.
Once that is done, the yarns are piled together to form one whole sewing thread. If the filament is made using polyester, the core takes up almost more than half of the thread like construction.

Step – 2: Ring Spinner
The dual-core spun yarn is being changed into the ring-spinning method. Once that step is done, the fibers are loose and expected to have somewhere between 40% to 50% of impurities. This is the carding process where the fibers can be mixed evenly.
It is done to ensure that the fiber can be introduced to the yarn more efficiently during the continuous process. Then, a single fiber is formed in a bundle parallelly. This step also ensures that the impurities are removed with solid adhesion.

Step – 3: Drafting
After the fiber strips have been processed mechanically, the distance between each of the fibers gets lower. All the filaments are forced in a way so that the aid can provide a feed curler that is suitable to the filaments. This makes the composition mixture and the color of the fiber more uniform.
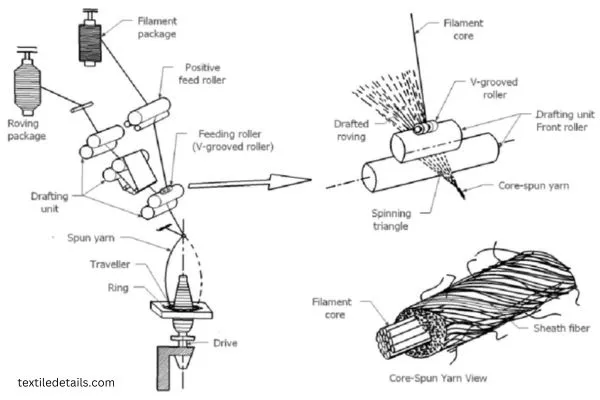
Step – 4: Stripping
The treater fiber strips are wounded to form appropriate packages for later processes. Then, the filaments enter through a curler into a nip factor. Where the cotton fibers pass through them, covering up the other filaments.
Step – 5: Roving
Then comes the roving process. The fiber strips are stretched according to their specific technical parameters in this step. This helps in improving the parallel elongation of the fiber. Meanwhile, the fiber also gets the appropriate twist and then gets wound into its shape. This is done so that the fibre can be stored and used in the following process.

Step – 6: Spinning
Now comes the spinning process. In this process, the roved fiber is spun to transform into the spun yard. While this happens, a proper twist is given to the fiber so that the spinning yarn can have a specific elasticity, gloss, feel, strength, and other mechanical and physical attributes.
This makes the spun yarn ready. However, there is another step that concludes the entire spinning process.

Post Processing
Even though the crucial task, which is the spinning of the spun yarn, is done, the spinning task is complete. But the entire spinning project is still ongoing. The post-processing process consists of four benefits:
- The internal performance of the final products is enhanced.
- The quality and appearance of the product are improved.
- The structural state of the product gets more stability.
- Appropriate roll form is made.
Different Spinning Methods
There are a lot of spinning methods which is available in the textile field. But, only some are suitable to spin for the core spun yarn manufacturing process. They are:
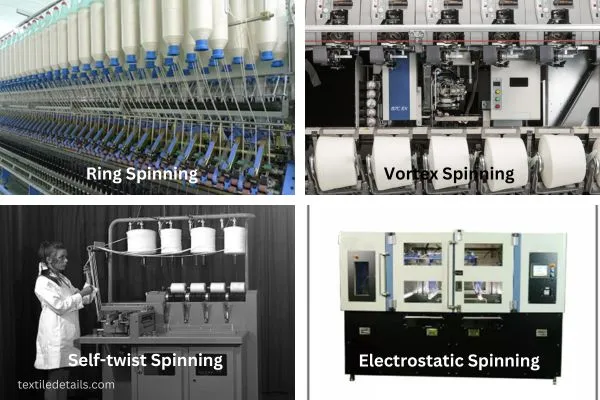
- Ring Spinning.
- Vortex Spinning.
- Self-twist Spinning.
- Electrostatic Spinning.
Any one of these will work for the core spun yarn manufacturing process.
Characteristics of Core Spun Yarn.
The core-spun yarn has taken the textile manufacturing industry to another level because of its unique qualities. There are some wide-ranging features of the core spun yarn which has secured it a high-ranking place in the garment industry.

These are some of the notable features that the core spun yarn has.
- Can recover to its original shape.
- It provides a lot of softness to the fabric.
- It is low maintenance and easy to care for.
- Offers better flexibility to the mixture.
- Comes with high tenacity, meaning will not tear upon force easily.
- In the case of physical attributes or size, the consistency is much greater.
- Quality product means that it comes with a much higher price, but it is worth it.
- The fibers are fire and heat-resistant to provide protection.
Final Words
One of the most well-known fabrics is woven corduroy, created using core-spun yarn. It is known to create a path that now produces stretchable and durable denim products. Denim apparel has gathered so much popularity worldwide because of the yarn that can be used to make good products. The yarn also provides many usages of applications in leather products, polyester, or cotton wrappers.
All of this has happened because of core spun yarn manufacturing. The process is fairly simple and does not take much time, making it easy for many factories to manufacture yarn. The cost is high, but there are a lot of usages so that the expense can be looked past.

Mahedi Hasan working as an Executive (Fabric Marketing) at Pengnuo Group. Graduated with B.Sc. in Textile Engineering. Before was a Top Rated content writer at Upwork, and Level 02 Seller at Fiverr, Level 02 Publisher at Ezoic. Very passionate about content writing, SEO practice, and fashion website designing. Highly Experienced fashion writer for the last 4+ years. Have extensive 7 years of experience in the wholesale clothing business.
