What is Combing?
Combing is a process of removing short fibers and sand impurities by using combs.
Comber: Comber is a machine by which fibers are combed.
Table of Contents
Types of comber:
1) Rectilinear combers: Used for cotton.
2) Circular combers: Used for worsted.
3) rotary combers: Used for spun silk.
4) Hacking Machines: These are used for the best fibers.
Objectives of combing:
The tasks of Comber’s are as follows:
1) Removing short fibers.
2) Removing neps.
3) Removing impurities.
4) Making fiber straight.
5) Producing a combed sliver.
Neps: Entanglement irregularities of fibers are called Neps.
Spinning Process Flow of Comb Yarn Manufacturing:
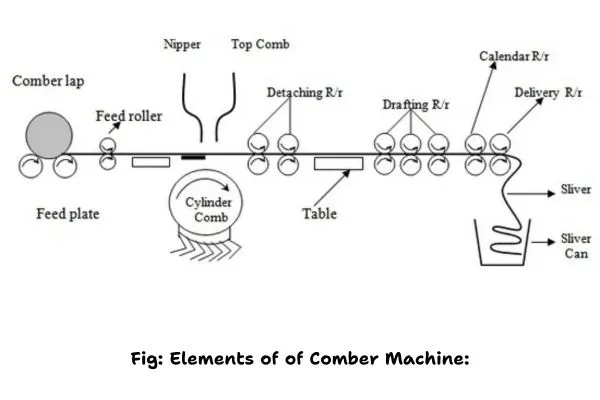
Comber Machine:
Elements of of Comber Machine:
- Detaching roller
- web
- Saw teeth
- Brush
- Top comb
- Top Nipper
- Feed roller
- Bottom Nipper
- Combing Cylinder
- Feed lap
- Supporting roller
Technical Data –
- Brand Name: Rieter
- Model: E – 62 / E – 65
- Origin: Switzerland
- No. of head: 8
- Input Material: Lap
- Output Material: Combed Silver
- Draft: 9 – 20
- Sliver Hank: 0.16- 0.24
- Production: Up to 80kg/hr
Combing Cycle / Sequence of Combing:
1) Lap feeding by feed roller-
The feed rollers ( f) move the lap web ( w) forward while the nippers ( Zb & Zt) are held open.
2) The top nipping by Nipper-
The top nipper ( Zt ) is lowered onto the bottom nipper ( Zb) so that the fibers are champed between them.
3) Combing by Cylinder-
The fiber fringe ( b) is combed by the combing cylinder.
* The fiber fringe – fiber protruding from the lap
4) Nipper Opening & forwarding-
The nippers open again & move toward the detaching rollers. (D).
5) Detaching Roller backward Movement-
The detaching rollers have returned part of the earlier drawn-off stock ( web V) by reverse rotation.
6) Piecing of web-
The projecting fiber fringe ( B) is placed on the returned web ( V)
7) Combing by top comb-
As the fibers are pulled through the needles of the top comb (T) during detaching, the trailing part of the fringe is combed.
8) Detaching roller forward movement-
The detaching rollers begin to rotate in the forward direction again & draw the clamped fibers out of the web (w)
9) Preparation for the next combing cycle-
The nippers open for the next feeding step & the top comb is withdrawn. A new combing cycle begins.
10) Waste extraction by brush-
The combining cylinder rotates continuously. The brush (A) that is mounted below the combining cylinder extracts all the waste ( impurities, neps, etc.)
Parameters Influencing the Combing Operation/Performance:
Parameters Influencing the Combing Operation:
1) Raw material
- fiber type
- fiber fineness
- fiber length
- fiber stiffness
- Uniformity of fiber length
- Moisture content
- Foreign Materials associated with the fibers
2) Material Preparation
- fiber parallelization
- Batt ( sheet) thickness
- Batt evenness
- Orientation of the hooks
3) Factors associated with the machine:
- Condition of machine
- Condition of comb
- Speeds
- Operational performance of comb
- Accuracy of settings
- Drafting arrangement
- Type of sliver-forming element
- Movement of elements
- Weight of elements
- Type of withdrawal of the combed web
4) Machine settings:
- Feed distance
- Type of feed
- Detachment setting
- Draft
- Drafting arrangement settings
- Piecing
- Point density of combs
- Circular comb clothing
Types of Feed in Combing Process:
1) Forward Feed / Con- current Feed
It means that feeding of the sheet into the nippers occurs while the nippers are moved towards the detaching rollers. When higher demands were made in production rates, it had to be used with noil % of up to 12%
2) Backward feed/counter Feed –
This means that the sheet is fed during the return of the nipper. When higher demands were made on quality, it had to be used with noil % of 12- 254%
What is the detaching index setting? What is the effect of this setting on combing?
The detaching (Detachment setting) index setting is the distance between the clamping line of the nippers & the nip line of the detaching rollers when these parts are at their closest spacing.
Wide detaching index setting results in a high level of noil elimination.
Contribution of Combing to Yarn Quality:
- Improve the spinning value of fiber.
- Improve the strength of yarn.
- Improve uniformity, smooth & luster of yarn.
- Improve efficiency in the next process.
- Reduce neps & hairiness of yarn.
- Reduce thick & thin places in the yarn.
- Produce short, trash-free yarn.
- Improvement of yarn quality
- Yarn imperfections
- Yarn evenness
- Yarn strength
- Noil elimination% ( combing)
Compare the Quality of Carded & Combed Yarn.
Compared with carded yarns, the combed yarns are –
1) Cleaner
2) More uniform
3) More compact
4) Stronger
5) Smoother( More lustrous)
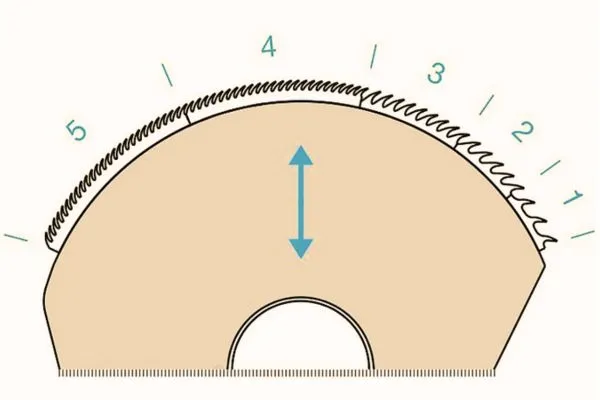
Circular Comb:
1) A cylinder drive shaft ( R) extends through the circular comb & carries one combing cylinder ( D) per combing head.
2) The combing cylinder in turn supports a combing segment ( s) which is bolted to the cylinder & is fitted with metallic clothing ( k).
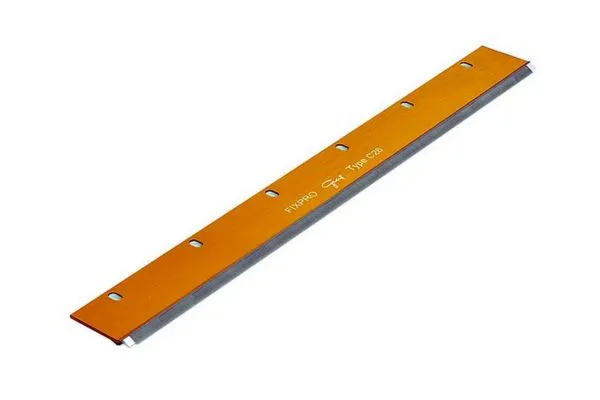
Top Comb :
1) The top comb usually comprises a holder ( H) to which screws secure the needle bar ( B).
2) The needle ( N) is soldered to the bar.
3) The needles have a flattened cross-section & a bend.

Degree of Combing :
The amount of oil extracted during combing expressed in percentage, is called the degree of combing.
Combination of Short Fibers, Neps & Impurities.
Types of combing:
According to degree of combing, there are 4 types of combing:
1) Scratch Combing – Up to 5%
2) Half Combing – Around 9%
3) Ordinary Combing – Between 10 – 18%
4) Full Combing – Greater than 18%
Factors of Degree of Combing:
1) Yarn Count – For a coarser count, a low degree of combing, and for a finer count, a high degree of combing is selected.
2) Amount of short fiber in the comber lap, For a high amount of short fiber, a high degree of combing is necessary.
3) Yarn Quality – For good quality yarn, the degree of combing should be 25%.
4) Production Cost – For a higher degree of combing, production costs become higher.

Mahedi Hasan working as an Executive (Fabric Marketing) at Pengnuo Group. Graduated with B.Sc. in Textile Engineering. Before was a Top Rated content writer at Upwork, and Level 02 Seller at Fiverr, Level 02 Publisher at Ezoic. Very passionate about content writing, SEO practice, and fashion website designing. Highly Experienced fashion writer for the last 4+ years. Have extensive 7 years of experience in the wholesale clothing business.
