The plain weave is obtained by raising all even-number warp ends at one pick and raising all the odd-numbered at the other pick. The repeat contains 2 ends and 2 picks. Both sides of the weave are similar.
Table of Contents
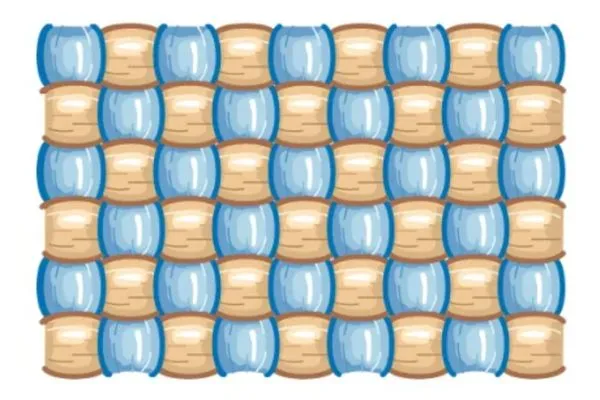
Characteristics of Plain Weave
- Made from all kinds of textile raw materials and yarns.
- Threads interlacing in an alternative order.
- Each thread gives the maximum amount of support to the adjacent threads.
- The texture is stronger and finer than any other ordinary cloth.
- Two heald shafts are sufficient to produce a plain weave when the number of ends is large, 4 and 6 heald shafts are used with skip draft.
Ornamentation of Plain Weave
- By using extremely fine yarn.
- By using coarse yarn.
- Threads of different colors are combined in check form.
- The threads in both warp and weft vary in color and in thickness.
- By using fancy slub yarn.
- By combining different orders of denting.
- Using two warp beams that are differently tensioned produced a “ Seer sucker stripe”.
- By using high twisted warp and weft yarn to produce crepe weave.
- By using different textile raw materials to produce union fabric.
Classification of Plain Cloth 1
Approximately square clothes:
- The cloths in which the warp and weft counts are the same.
- The ends and picks per inch are equal.
- The warp and weft cover factors are approximately equal.
- The warp and weft are equally prominent.
- The crimps are also equal.
150 x 150
———- x 58”
40 x 40
Classification of Plain Cloth
Warp Faced Cloths:
- The clothes in which the warp cover factor is more than weft.
- The ends are more than the picks per inch.
- The warp is prominent on both sides.
- The warp yarn is finer than the weft yarn.
150 x 30
———- x 56”
50 x 8
Classification of Plain Cloth
Weft Faced Cloths:
- The clothes in which the weft cover factor is more than warp.
- The picks are more than the ends per inch.
- The weft is prominent on both sides.
- The weft yarn is high-quality than the warp yarn.
32 x 148
———- x 57”
7 x 60
Another Classification
1 . Balanced cloth
- The clothes in which the warp and weft count are the same.
- The ends and picks per inch are equal. c. The warp and weft cover factors are approximately equal.
- The warp and weft are equally prominent. e. The crimps are also equal.
150 x 150
———- x 58”
40 x 40
Another Classification
2. Unbalanced cloth
- The ends and picks are the same but the warp and weft counts are different.
- The warp and weft counts are similar but the ends and picks per inch are different.
- The warp and weft counts and the ends and picks per inch are different.
- Derivatives of plain weave Plain
- Rib Matt Warp rib Weft rib Regular Irregular StitchFancy
Warp Rib
- It produces a rib or cord effect in the weft direction.
- Finer yarn is used as warp and coarser yarn is used as weft yarn.
- The number of ends is more than the number of picks in unit space.
- Low twisted yarn is used as weft.
- Warp yarn single yarn and weft yarn bundle or grouped yarn.
- Regular: F. N. X/X
- Irregular: F. N. X/Y

Weft Rib
- It produces a rib or cord effect in the warp direction.
- Finer yarn is used as weft and coarser yarn is used as warp yarn.
- The number of picks is more than the number of ends in unit space.
- Low-twisted yarn is used as a warp.
- Weft yarn single yarn and warp yarn bundle or grouped yarn.
- Regular: F. N. 1/1 (x)
- Irregular: F. N. 1/1 (x+y)

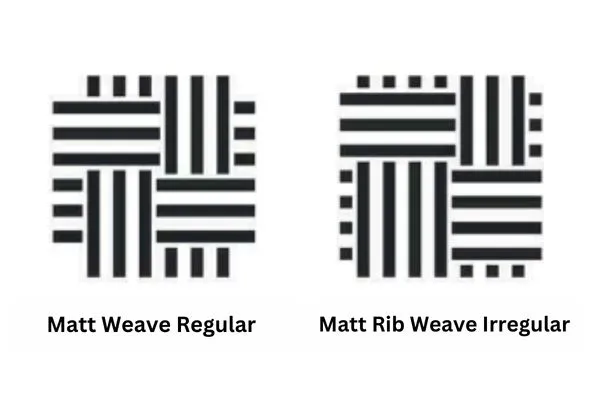
Matt Weave
- Matt weave is constructed by extending the plain weave in both warp and weft directions.
- Combination of warp and weft rib.
- Loose structure.
- Matt weaves tend to give a smooth surface of the fabric and more flexible fabrics than plain weaves.
- Regular: F. N. x/x (x)
- Irregular: F . N. x/y (x+y)
- Stitched: F. N. x/x (x)
- Fancy: F. N. x/x (x)

Satin weave
- The fabric surface is very smooth and lustrous.
- By using low twisted yarn and by increasing EPI, smoothness can be increased.
- Only one interlacement between one warp and one weft.
- This interlacement point is covered with an adjacent long float of yarn.
- Loose structure compared to plain and twill weave.
- No visibility of the twill line in this weave.
- Widely used in the case of jacquard design.
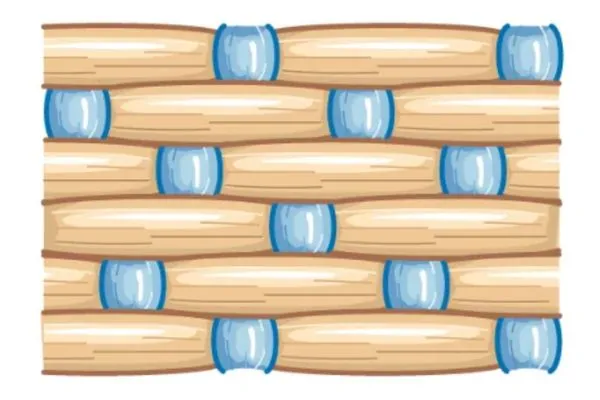
Classification of Satin
- Warp satin
- Weft sateen
- Regular
- Irregular

Mahedi Hasan working as an Executive (Fabric Marketing) at Pengnuo Group. Graduated with B.Sc. in Textile Engineering. Before was a Top Rated content writer at Upwork, and Level 02 Seller at Fiverr, Level 02 Publisher at Ezoic. Very passionate about content writing, SEO practice, and fashion website designing. Highly Experienced fashion writer for the last 4+ years. Have extensive 7 years of experience in the wholesale clothing business.
