What is Singeing?
Singeing: The verb ‘singe’ literally means ‘to burn superficially’. Technically, singe refers to the burning-off of loose fibers. Singeing is a process by which projecting or floating fibres, that stand out on the surface of the fabric are burned off.
Singe is an important part of the fabric pre-treatment process. If it is not done properly, may yield unclear print patterns, mottled fabric surfaces & pilling results. Textile materials are most commonly singed in woven or knitted fabric form or in yarn form.
Table of Contents
Objective:
✔ To remove hairy fibers projecting on the surface of cloth and give a smoothen face.
✔ Optical levelness of the dyeing and clean-out lines of a printing design.
✔ To resist the soiled-off nature of the hairy fabric.
✔ To increase luster in the finished fabric.
✔ To prepare the fabric for the next process.
Importance
▪ Cotton materials are valued for their smooth appearance. After the formation of fabric, it has a fuzzy or hairy appearance due to projecting fibers, thus affecting the luster & smoothness.
▪ Unsigned fabrics are soiled easily.
▪ The protruding fibers obstruct the subsequent dyeing and printing process.
▪ Cotton materials that are to be mercerized are signed to maximize the luster.
▪ In fabrics of polyester & cellulosic fiber blends, singe is the best method to control pilling. Sometimes double singe is done to minimize the pilling.
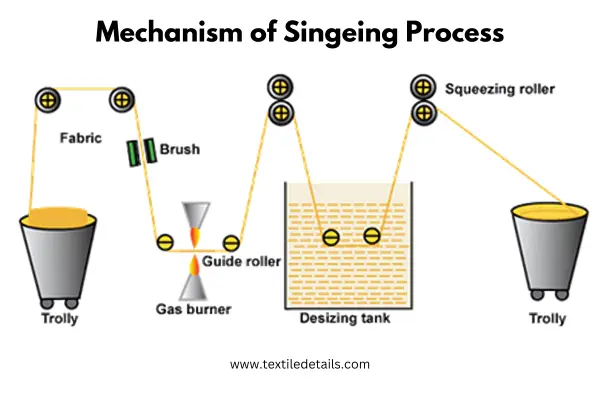
Mechanism of Singeing Process:
Brushing: To produce a smooth surface finish on fabrics made from staple fibers first the fabric surfaces are brushed lightly to raise the unwanted fiber ends.
Burning off: Then the fabric is singed with or passed over heated copper plates or open gas flames. The fiber ends burn off. The fabric is moved very rapidly, and only the fiber ends are destroyed.
Cooling: As soon as the fabric leaves the singe area, it enters a water bath or de-sizing bath. This stops any singe afterglow or sparks that might damage the cloth.
Precautions during Singeing:
a) The fabric to be singed should be dry as wet fabric tends to scorch more readily than dry. b) Uneven singe may cause streaks or bubbles on fabric when the fabric is finished.
c) Improper singe may lead to up to 75% tensile strength loss in warp direction.
d) The fabric should not contain any acid-releasing salt, which may release acid when heating and tendering the fabric.
e) Stopping the machines may cause bars on the fabrics.
f) Singeing may cause hardening of the size thus leading to difficulty in its removal.
g) Possibility of thermal damage to temperature-sensitive fabrics, as heat-sensitive fibers may melt forming tiny balls on the surface. These balls interfere with dye absorption, so that, as a general rule, heat-sensitive fibers would be singed after dyeing or printing.
Classification of Singeing Machines:
- Plate singeing machine
- Rotary-cylinder or Roller singeing machine
- Gas singeing machine

Plate Singeing Machine:
In this singeing machine, the cloth passes over & in contact with one or two heated curved copper plates. The thickness of the plates ranges from 1-2 inches.
Working Principle:
▪ Heating of plates is done by a suitable burning arrangement of gas mixed with air.
▪ The cloth passes over & in contact with the plates at a speed of 150-250 yards per minute.
▪ The passage of the cloth can be arranged in such a manner that one or both sides of the fabric may pass over and in contact with the heated plate, in order to accomplish the singeing of one or both sides in a single passage.

▪ To avoid local cooling of the plate, an automatic traversing mechanism is fitted to the machine.
This mechanism brings the cloth into contact with a constantly changing part of the plate, not only to avoid local cooling but also local wearing of the plate.
Advantages:
✔ Very suitable for the back filter in the finishing process.
✔ A certain amount of luster is produced due to friction.
✔ Uniform singe.
Disadvantage:
✔ Very difficult to maintain the proper heat control of the plate.
✔ Discontinuous process so more time taken.
✔ More labor cost.
✔ Not uniform singeing in stitch portion.
Roller Singeing Machine:
In this type of singe machine, the cloth passes over and comes in contact with a heated rotary cylinder made of copper or cast iron which has internal firing.
Working Principle:
▪ The rotary cylinder revolves slowly in the opposite direction of the fabric so that protruding fibers are raised & constantly a fresh surface of the roller comes in contact.

▪ If the singe of both sides of the fabric is required, then two cylinders are employed, one for each side of the fabric.
Advantage:
✔ The surface temperature of the cylinder is more uniform than that of the plate singeing machine.
✔ This method is very suitable for velvet & pile fabrics.
✔ Uniform singeing.
✔ Luster increase.
Disadvantage:
✔ Only one side of the fabric is singed. Both side singeing arrangements are complex.
✔ Due to overuse, a small tinny groove was created on the cylinder.
✔ Local cooling may arise on the cylinder due to contact between cold fabric & cylinder surface.
Gas Singeing Machine:
Gas Singeing Machine: In this type of singe machine, the fabric passes over a burning gas flame at such a speed that only the protruding fibers burn and the main body of the fabric is not damaged by the flame. This is the most common type of machine used for singe.
Working Principle:
▪ There are four burners, which is capable of singe one or both surfaces of the fabrics.
▪ A water-cooled roller is provided at a location opposite to the burners, so as not to undermine the strength of even thin fabrics. Drain temp. of the water-cooled roller ranges of 50-55° C.

▪ Cautions are required because a dew-point is generated when the water-cooled roller is cooled down too much, and this results in an increased amount of remaining fuzz or adhered carbon.
▪ The fabric feed speed: 100-150 m/minute.
Important Considerations during Gas Singeing:
a) The flame should be more bluish (less yellowish) to give the maximum temperature.
b) Regulate the fabric speed according to the fabric construction, thickness, weight, etc.
c) The burner nozzles must be free from choking. Choking of nozzles may result in the appearance of haziness which becomes apparent after dyeing.
d) The width of the flame is set to cover just a little more than the fabric width. This will ensure the conservation of energy.
e) The exhaust blowers over the burners are to be in proper operation. If not, it can lead to the re-deposition of the burnt-out fibers on the fabric causing black specks.
f) Ensure appropriate quenching into water/desize bath after singe. Otherwise, entrapped smoldering particles may lead to fabric getting burnt & create holes on the surface.
g) Guide rolls next to the flames or the guide rollers on which flame is directed in case heat-sensitive fabrics should be cooled, generally by cold water circulating through the guide rollers. Otherwise, they could become red hot and scorch the fabric.
Parameters to be controlled in Gas Singeing Machine:
- Flame Intensity: Flame intensity is based on the amount & the outlet speed of the gas-air mixture leaving the burner slots. The temperature of the flame ranges from 1250 to 1300̊C & the speed ranges from 15 to 35 meters/second. The flame intensity lies between 5 and 20 bars. All burners must produce a uniform flame.
- Fabric Speed: The fabric speed is in the range of 50-160 m/min depending on fabric GSM (gram per square meter) & fiber blend. For heavier fabrics, the speed is kept slower. 3. Singeing Position: The position of fabrics while the flame bounces may be as follows: a. Singeing onto free-guided fabric: Highest efficiency, all fabrics.
- Singeing onto water-cooled roller: Less weight & open structure fabrics. c. Tangential Singeing: Very lightweight and sensitive fabrics.
- Distance between Flame Burner & Fabric: The distance between the burner & fabric can be adjusted in a range from 6-20mm.
- Flame Width: All good singeing machines come with a provision of flame width adjustment according to the width of the fabric.
Advantages of Gas Singeing Machine:
✔ Both sides singeing in this process.
✔ Uniform temperature can be controlled over roller and plate singe_ing.
✔ In gas singeing, brush is used which stands the lying projecting the fibers but not in plate and roller singe.
✔ No plate decay in gas singe_ing, but decay in plate and roller singe.
✔ It is a standard process and ideal singe.
✔ It is a continuous process, so no hamper in production.
✔ After singeing the fabric is dipped in the water tank hence app sparks are extinguished.
✔ Fabrics in the inter-stitches are singed well.
✔ Fabric becomes very suitable for subsequent processes.
Disadvantages of Gas Singeing Machine:
✔ Not suitable for synthetic fiber.
✔ A dirty burner can produce a spot on the fabric.
✔ Due to inconsistent speed, the fabric may get burnt.
✔ Some common problems may occur as follows:
o Incomplete Singeing,
o Over-singing,
o Uneven Singe_ing,
o Stripes,
o Formation of Small Beads of Molten Material etc.
Common problems in Gas Singeing and their causes:
- Incomplete Singe_ing: Incomplete singe occurs due to
- Low flame intensity, faster fabric speed, or too far distance between fabric & burner 2. Inappropriate (i.e. less severe) single-position
- Too much moisture in the fabric is coming for singing.
- Over-singing or Thermal Damage of Fabric: Occurs due to
- Too high flame intensity or too slow fabric speed.
- Too close distance between fabric & burner.
- Inappropriate (i.e. too severe) single-position
- Uneven Singeing: Occurs due to
- Non-uniform in moisture content or flame intensity.
- Change in fabric speed, flame height or distance between fabric & burner. 3. Uneven smoke evacuation over the burners.
- Uneven supply of gas-air mixture.
- Horizontal & Vertical Stripes: Occurs due to
- Rollers with an un-centered rolling action.
- Sudden fabric tension increases.
- Total or partial blockage of flame outlet.
- Formation of Small Beads of Molten Material: Occurs due to
- Insufficient energy supply is when the thermal energy is not supplied quickly enough to be able to ignite the thermoplastic fiber rather than melt it.
- Unsuitable temperature for heat-sensitive fabrics.
Comparison between different Singeing Methods:
| Topics | Gas Singeing | Plate Singeing | Roller Singeing |
| Singeing Mechanism | The fabric passes over a burning gas flame. | Burning gas mixed with air. | The fabric passes over & in contact with heated rotary copper cylinder. |
| Burning arrangement | Gas burner. | The fabric passes over & in contact with heated rotary copper cylinder. | Internal firing in cylinders. |
| Fabric speed | 250 – 400 yd/min | 150 – 250 yd/min. | Slowly passed. |
| Surface Motion | Only fabric moves. | The fabric passes over & in contact with heated curved copper plates. | Automatic traversing mechanism for plates. |
| Temp. control | Uniform | Not uniform | Not uniform |
| The fabric passes over & in contact with a heated rotary copper cylinder. | By brushing. | No mechanism. | The cylinder surface may decay for friction |
| Surface decay | No decay | Opposite direction of cylinder revolving. | The cylinder revolves slowly in the opposite direction. |
| Fabric luster | Extra luster is not produced | Metal surface friction causes extra luster | Metal surface friction causes extra luster |
Other questions
❖ Why Gas singeing is preferable to plate & roller singeing.
❖ Singeing is essential- why?
❖ Discuss faults of fabrics with causes & remedies on singeing.
❖ Singeing process may be substituted by which process?
❖ If the fabric is not singed properly, what problems may arise during dying finishing?
Singeing Lecture
by TARIQUL ISLAM
Wet Preparatory Process Lecturer
Textile Engineering College Chittagong (CTEC)

Mahedi Hasan working as an Executive (Fabric Marketing) at Pengnuo Group. Graduated with B.Sc. in Textile Engineering. Before was a Top Rated content writer at Upwork, and Level 02 Seller at Fiverr, Level 02 Publisher at Ezoic. Very passionate about content writing, SEO practice, and fashion website designing. Highly Experienced fashion writer for the last 4+ years. Have extensive 7 years of experience in the wholesale clothing business.
