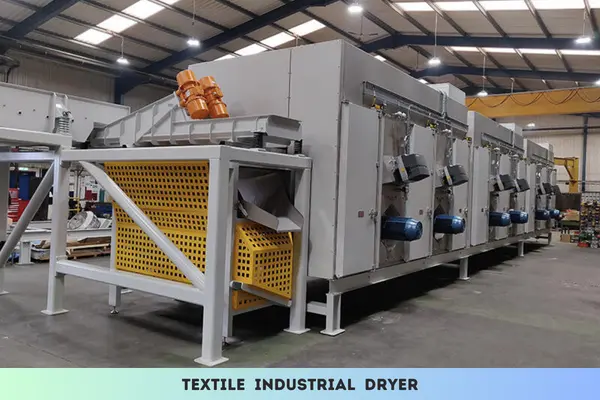
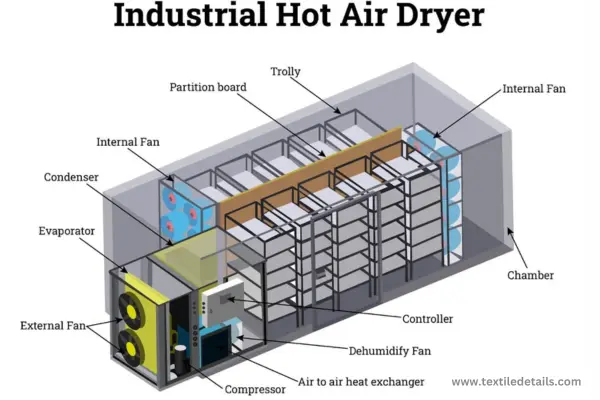
Textile industrial dryer is a new generation design for highly efficient use of heat and saving energy, widely used in laundry, dyeing factories.
In the fast-paced world of textile manufacturing, the efficiency of fabric drying plays a pivotal role in determining production timelines and product quality. The emergence of Textile Industrial Dryers has marked a significant shift from traditional drying methods, introducing advanced technologies that not only expedite the drying process but also enhance overall production capabilities.
Table of Contents
Main Features of Textile Industrial Dryer

- Digital control panel.
- In a heat exchanger, cold air will be heated by steam pipes, to make full use of the steam and condensate water.
- Ball value can automatically discharge cold water.
- Equipped with a specially designed cold air door, the cooling step will not take away the heat from the steam pipe, cooling faster and saving more energy.
- Gentle heating mode, suitable for sensitive fabrics.
| Models | GZP – 40 | GZP – 70 | GZP – 100 | GZP – 150 | GZP – 200 | GZP – 300 | GZP – 400 | |
| Capacity | lbs | 40 | 70 | 100 | 150 | 200 | 300 | 400 |
| Drum diameter | mm | 700 | 940 | 970 | 1080 | 1380 | 1800 | 1800 |
| Drum depth | mm | 450 | 760 | 980 | 1065 | 1100 | 1100 | 1200 |
| Drum volume | lt. | 170 | 520 | 720 | 970 | 1640 | 2800 | 3050 |
| Spin speed | rpm | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 28 | 28 |
| Steam connection | θ | DN25 | DN25 | DN25 | DN25 | DN25 | DN25 | DN25 |
| Steam max pressure | Bar | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| Air max pressure | Bar | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 |
| Power of motor | KW | 0.75 | 0.75 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 2.2 | 3 | 4 |
| Blower motor | KW | 0.75 | 0.75 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 4.4 | 4.4 | 5.2 |
| Total power | KW | 1.3 | 1.3 | 3.7 | 3.7 | 6.6 | 7.4 | 9.2 |
| Voltage | Volt/Hz | 380/50 | 380/50 | 380/50 | 380/50 | 380/50 | 380/50 | 380/50 |
| Steam consumption | kg/h | 25 | 56 | 82 | 120 | 165 | 220 | 300 |
| Natural gas consumption | kg/h | 0.75 | 1.1 | 1.6 | 2.5 | 3.7 | ||
| Machine length | mm | 1000 | 1250 | 1500 | 1900 | 2140 | 2100 | 2200 |
| Machine width | mm | 830 | 1000 | 1100 | 1200 | 1560 | 1860 | 1900 |
| Machine height | mm | 1720 | 2000 | 2200 | 2450 | 2550 | 2650 | 2650 |
| Machine weight | kg | 350 | 500 | 500 | 800 | 1100 | 1250 | 1350 |
| Energy saving | % | 0 | 0 | 15 | 20 | 20 | 25 | 25 |
Optional Heating system
- Gas heating / Electrical heating
- Gas pressure: 3 – 4 KPA
Gas consumption:
3.0 – 4.0 m3/h (GZP – 400)
3.0 – 3.5 m3/h (GZP – 300)
2.0 – 3.0 m3/h (GZP – 200)
1.5 – 2.5 m3/h (GZP – 100)
Optional Function
- Humidity
- Dust screen for easy cleaning
Evolution of Textile Drying Technologies
Traditional Drying Methods
In the early days of textile manufacturing, drying involved time-consuming processes like air-drying and sun-drying.
These methods, while effective, posed challenges in terms of consistency and speed.
Challenges Faced in Conventional Processes
Traditional drying methods often led to issues such as uneven drying, fabric shrinkage, and prolonged production times. These challenges necessitated the need for more sophisticated drying technologies.
Emergence of Textile Industrial Dryers
The advent of Textile Industrial Dryers addressed the shortcomings of traditional methods. These modern machines utilize advanced drying mechanisms, providing a solution to the perplexities faced by manufacturers.
Importance of Modern Textile Industrial Dryers
1. Advanced Drying Mechanisms
Textile Industrial Dryers employ cutting-edge technologies such as hot air drying, infrared drying, and even microwave drying.

These mechanisms ensure faster and more uniform drying, improving overall efficiency.
2. Energy Efficiency
One of the standout features of these dryers is their energy efficiency. With the global push towards sustainability, textile manufacturers are increasingly turning to energy-efficient drying solutions to reduce their environmental footprint.
3. Customization for Various Fabrics
Modern dryers are designed to handle a diverse range of fabrics. Whether it’s delicate silk or sturdy denim, these machines can be customized to suit the specific drying requirements of different materials.
Benefits of Using Textile Industrial Dryers
a. Increased Production Speed
The efficiency of Textile Industrial Dryers translates to a significant boost in production speed.

Manufacturers can now meet tight deadlines without compromising on the quality of the dried fabric.
b, Cost-Effectiveness
While the initial investment in these advanced dryers may seem substantial, their long-term cost-effectiveness is undeniable. Reduced energy consumption and increased productivity contribute to a favorable return on investment.
c. Improved Fabric Quality
Uniform drying offered by modern industrial dryers results in improved fabric quality. The risk of defects such as wrinkles, uneven texture, or color variations is minimized, leading to a higher-quality end product.
Types of Textile Industrial Dryers
1. Hot Air Dryers
These dryers use heated air to evaporate moisture from fabrics, ensuring a rapid and efficient drying process.

They are suitable for a wide range of materials and are commonly used in large-scale textile production.
2. Infrared Dryers
Infrared dryers use infrared radiation to penetrate and heat the fabric, providing a quick and uniform drying experience. They are particularly effective for heat-sensitive materials.
3. Microwave Dryers
Microwave dryers utilize microwaves to generate heat within the fabric, resulting in a swift and energy-efficient drying process. They are gaining popularity for their ability to handle delicate fabrics with care.
Choosing the Right Textile Industrial Dryer
i. Consideration of Fabric Type
Different fabrics have distinct drying requirements.
Manufacturers need to choose a dryer that caters to the specific needs of the materials they work with.
ii. Production Scale
The scale of production is a crucial factor in selecting the right dryer. Small-scale operations may benefit from compact, versatile dryers, while large-scale manufacturers might require high-capacity machines.
iii. Energy Efficiency Ratings
As sustainability becomes a focal point in industrial practices, checking the energy efficiency ratings of dryers is essential. Opting for machines with high efficiency not only reduces environmental impact but also lowers operational costs.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Overcoming Fabric Shrinkage
Fabric shrinkage is a common concern in textile drying.
Advanced dryers come equipped with features that minimize shrinkage, such as controlled temperature settings and precise moisture sensors.
Addressing Uneven Drying
Uneven drying can lead to product defects. Modern dryers are designed with features like airflow control and multiple heating zones to ensure that every part of the fabric receives uniform drying.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Regular cleaning, inspection, and calibration are essential for the longevity of textile industrial dryers. Manufacturers should implement routine maintenance schedules to prevent breakdowns and ensure consistent performance.
Industry Applications
a. Apparel Manufacturing
Textile industrial dryers are widely used in the apparel industry to dry fabrics like cotton, polyester, and blends. The speed and efficiency of these dryers contribute to the timely production of clothing items.
b. Home Textiles
From bed linens to curtains, home textile manufacturers benefit from the versatility of industrial dryers. Different settings allow for the careful drying of various materials used in home furnishings.
Technical Textiles
Industries producing technical textiles, such as automotive fabrics or industrial filters, rely on the precision and customization capabilities of modern drying technologies.
Environmental Impact of Textile Industrial Dryers
Sustainable Drying Practices
Manufacturers are increasingly adopting sustainable drying practices, such as using renewable energy sources and implementing heat recovery systems. These initiatives aim to reduce the environmental impact of textile production.
Eco-Friendly Drying Technologies
Innovation in eco-friendly drying technologies, including the use of recycled materials in dryer construction, contributes to the industry’s commitment to sustainability.
Future Trends in Textile Drying
- Integration of IoT in Drying Processes: The Internet of Things (IoT) is making its way into textile industrial dryers, enabling real-time monitoring and control. This integration enhances operational efficiency and allows for predictive maintenance.
- Advancements in Heat Recovery Systems: Efforts are underway to improve heat recovery systems in dryers, maximizing energy utilization and minimizing waste. This not only reduces operating costs but also aligns with global sustainability goals.
- Robotics in Fabric Handling: The incorporation of robotics in fabric handling is streamlining the drying process further. Automated systems ensure precise and efficient movement of fabrics through the drying stages.
Tips for Optimal Performance and Maintenance
Regular Cleaning and Inspection
Routine cleaning and inspection of dryers prevent the accumulation of dust and debris, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.

Calibration for Precision
Calibrating temperature and moisture settings regularly ensure precise drying, minimizing the risk of fabric damage or defects.
Staff Training for Efficient Operation
Proper training for machine operators is crucial for efficient and safe dryer operation. Well-trained staff can identify and address issues promptly, reducing downtime.
Market Overview and Key Players
Growth Trends in Textile Drying Industry
The textile drying industry is witnessing steady growth, driven by the demand for faster and more sustainable production processes. Emerging economies are becoming key players in this market.
Leading Manufacturers and Innovators
Companies like GZP Drying Systems and Innovate Textile Tech are at the forefront of innovation in textile drying. Their commitment to research and development ensures that the industry keeps evolving.
Conclusion
In the dynamic landscape of textile manufacturing, the adoption of Textile Industrial Dryers represents a pivotal step towards enhanced efficiency, sustainability, and quality. As the industry continues to evolve, these advanced drying technologies will play a crucial role in shaping the future of fabric production.
The FAQs
How do Textile Industrial Dryers contribute to sustainable practices?
Textile Industrial Dryers contribute to sustainability by incorporating energy-efficient mechanisms and eco-friendly technologies, reducing the overall environmental impact of textile production.
Are there specific dryers for different types of fabrics?
Yes, modern industrial dryers are designed to be versatile and can be customized to suit the drying requirements of various fabrics, from delicate silk to sturdy denim.
What maintenance practices are crucial for the longevity of industrial dryers?
Regular cleaning, inspection, and calibration are essential maintenance practices to ensure the optimal performance and longevity of industrial dryers.
How do Textile Industrial Dryers address common challenges like fabric shrinkage?
Advanced dryers come equipped with features such as controlled temperature settings and precise moisture sensors to minimize fabric shrinkage.
What role does the Internet of Things (IoT) play in textile drying?
The integration of IoT in textile industrial dryers enables real-time monitoring and control, enhancing operational efficiency and allowing for predictive maintenance.

Mahedi Hasan working as an Executive (Fabric Marketing) at Pengnuo Group. Graduated with B.Sc. in Textile Engineering. Before was a Top Rated content writer at Upwork, and Level 02 Seller at Fiverr, Level 02 Publisher at Ezoic. Very passionate about content writing, SEO practice, and fashion website designing. Highly Experienced fashion writer for the last 4+ years. Have extensive 7 years of experience in the wholesale clothing business.
